Southern Taiwan Global Research
& Industry Alliance
A new laser acupuncture device which offers therapeutic functions currently unavailable in other laser acupuncture systems
Available to license


Introduction
Acupuncture had a market size of USD 24 Bn in 2017 and it continues to gain significant interest worldwide as a result of the increasing demand for non-invasive therapies. Researchers have invented a new-generation laser acupuncture system which can offer true therapeutic effects of reinforcement and reduction via programmable lifting and thrusting functions.
Our Technology
Acupuncture is the therapeutic practice of inserting thin needles into the body. It originates from Chinese medicine and is a particularly popular therapy in countries including China, Japan, and Korea. Extensive studies have shown its potential utility and acupuncture has been proven to be an effective treatment for a wide range of conditions such as headache, lower back pain, and morning sickness.
Acupuncture works by stimulating specific points on the body to improve circulation, regenerate cells, and reduce inflammation. It is believed that the stimulation is induced not simply because needles are inserted through the skin but because the needles are also subject to manipulation techniques including lift, thrust, and twist.
Researchers at I-Shou University have invented a laser acupuncture device which is capable of mimicking these techniques in a manner which can not be achieved by other laser or electro-acupuncture systems. The desktop size of the device means that it can easily be deployed in hospitals, speciality clinics, and wellness centers.
Features and Benefits
The new laser acupuncture system has the following advantages:
- Minimally invasive technique using cold laser
- Improved efficacy while still offering the therapeutic functions used in traditional manual acupuncture
- Personalised treatment: the system is software controlled and customisable for each patient
- Small size for wide deployment
- Functions include “Pull” “Push” and “Twist”, which were previously not achievable using other laser or electro-acupuncture systems
Current Status
This project is at TRL 3 – a prototype was built as an accessory add on to conventional laser equipment and limited experimental data is available. Several patents have been granted in Taiwan.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
James Hudson, PhD
E: james.hudson@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7971 515869
Hyaluronan-modified hydrogel for the treatment of articular cartilage defects
Available to license, collaborate or invest
Introduction
Because there are natural limitations to the healing of cartilage, there is a particularly strong demand for improved treatment outcomes when dealing with cartilage damage. One promising approach involves the use of hyaluronan-modified hydrogel in which mesenchymal cells are promoted to convert to cartilage cells within the damaged region. A research team at the Kaohsiung Medical University (KMU) in Taiwan has shown that hyaluronan-modified hydrogel with optimal chemical and physical cues is able to enhance the repair of cartilage while also providing additional patient benefits compared with the direct use of stem cells.
The KMU Team is now looking to progress the development and validation of this technology with industrial partners.
Our Technology
Research at KMU has explored the application of hyaluronan-modified hydrogel to enhance repair of cartilage damage without using stem cells. This research has led to the development of a suite of technologies comprising:
- A photo-crosslinked hyaluronan-modified hydrogel.
- An injectable hyaluronan-modified hydrogel.
These technologies may be applied together to provide a platform solution.
This platform has been validated in an animal (rabbit) trial. The project team are now seeking to pursue a larger animal study in collaboration with the right industry partner.
Project Status
This is project is at TRL 3-4 and the technology has been validated in a small animal study. Patents covering the use of a hyaluronan-modified hydrogel have been applied for via PCT and in Europe, USA, China and Japan.
Features and Benefits
The use of hyaluronan-modified hydrogel for the promotion of cartilage repair provides the following features and benefits:
- Enhanced chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells
- Increased healing of damaged cartilage
- Ease of application compared with mesenchymal stem cells
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
James Hudson, PhD
E: james.hudson@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7971 515869
Novel laser-based manufacturing process to produce high quality diffraction gratings
Available to license
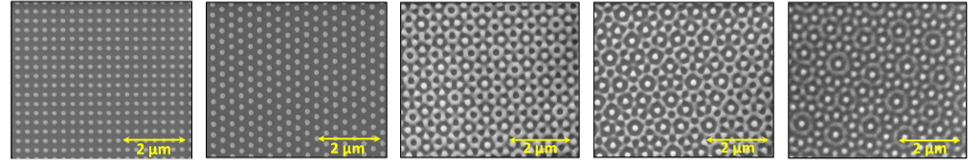
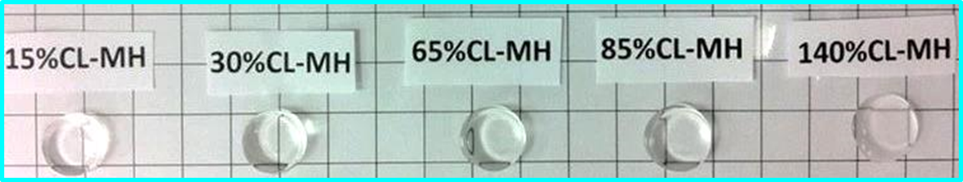
Introduction
Laser lithography may be used to pattern surfaces to produce diffraction gratings for applications in optical devices and spectrophotometers. A common limitation of this technique is compromisation of the resolution of the grating structure because of undesirable patterns of incident laser light. A research team at National Sun Yat-sen University (NSYSU), Taiwan, has developed an advanced laser lithography technology that avoids these limitations and produces diffraction gratings of exceptional quality. The technology is comprehensively supported by a complementary suite of fabrication and metrology solutions.
The NSYSU research team are now seeking to commercialise these laser lithography technologies internationally.
Our Technology
Research at NSYSU has delivered improved laser lithography techniques for the patterning of surfaces at high spatial resolution and at high speed. A key application of this technology is in the production of diffraction gratings within industrial processes.
To produce superior diffraction gratings, the research team apply a flat-top laser beam that is produced by the combination of two collimated laser beams of different size such that Gaussian-related intensity losses are prevented. Grating structures which are uniform over a 4-inch wafer with a duty cycle variation of less than 5% may be produced (and imaged for quality control purposes) within seconds.
This technology is complemented and enabled by a suite of metrology and software solutions that are available for immediate transfer to third parties for commercial exploitation.
Features and Benefits
The diffraction grating manufacturing techniques provide the following features and potential benefits:
- Reduction in Gaussian distribution of incident laser light
- Increased structural resolution of surface patterning
- Mask-free patterning of large areas
- Compatibility with a proprietary grating mapping to provide quality control monitoring in real time.
Project Status
This project is at TRL 9. It has been exploited in the market place. Patents covering the technology are in force including in the USA.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
James Hudson, PhD
E: james.hudson@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7971 515869
Programmable optical film for control of window transparency
Proposed New Spin-Out Company

Introduction
An innovation from the National Sun Yat-sen University (NSYSU) is paving the way for windows to become transparent displays that may be used for advertising and other media applications. In addition, the occupants may achieve smart control of the window’s optical properties such that light entering the building is regulated. This optical control has important applications including opaqueness (allowing for total darkness by preventing light from entering) and blurring (such that light passes through the window while simultaneously ensuring that the occupants can not be discerned from an external view). The NSYSU research team are now seeking to spin-out this disruptive technology into a new company.
Our Technology
Conventional smart window products have three critical challenges. One is that it only has single function which do not meet all of the user’s needs. Another is the high cost by glass replacement because of the non-standardised window including different size, shape, material, etc. A third is that the film is dark when the electrical current is off.
The multi-functional smart films can be directly laminated onto existing window glass so that the glass becomes electrically switchable among transparent, tinted, privacy protection, and image display states. Remote control of the smart window is easily done by connecting it to a smart phone or switch through WiFi, Bluetooth, etc. It has overcome the major challenges of current smart windows, including single function and high cost of glass replacement. These smart window films have also found their widespread use in smart homes, business buildings, and vehicles.
They have made a significant breakthrough which creates the possibility of applying the principals of smart glass to any window.
The research group is now increasing the accessibility of this technology through manufacturing.
Features and Benefits
The novel smart window coating provides the following features and potential benefits:
- Retrofittable to existing windows
- Control of thermal and optical properties
- Ultrafast response times
- Allows windows and glass to take on the auxiliary functions of advertising boards or decorative features
Project Status
This is project is at TRL 7. Large scale manufacture and roll-out is being progressed. Multiple patent families covering the technology are in force.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
James Hudson, PhD
E: james.hudson@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7971 515869
Record-beating, nano-structured and residue-free adhesives inspired by nature.
Available to license

Introduction
Conventional adhesives and adhesive materials utilise a glue film that may leave a sticky residue on the attached surface. In some applications, this residue is merely inconvenient but, in others such as in semiconductor manufacturing, it creates significant technical issues. To address these limitations, researchers at the National University of Kaohsiung (NUK) have looked to structures present in nature that provide strong adhesive properties without leaving any residue. These structures have been reproduced using nanotechnology. The result is a number of new adhesive solutions which are noted for their strength, utility and residue-free properties.
The NUK Team is now looking to commercialise these adhesives by including them in products.
Our Technology
Research at NUK has elucidated the behaviour of various surfaces and appendages found in nature, including gecko feet & octopus suckers and characterised how Van der Waals forces may create attractive/adhesive properties. These studies have highlighted how adhesive forces are created by micro/nanostructures that may be replicated using advanced fabrication techniques.
The research has realised the strongest dry adhesive described to date (50N/m2) but it has also led to an ability to design the nano-structured surface to provide control over the precise adhesive strength. This ability to control adhesion opens up tailored applications in both domestic and industrial settings, including biomedical applications.
The research group is now increasing the accessibility of this technology by exploring how it may be exploited via reel-to-reel manufacturing methods and is seeking industrial collaboration.
Features and Benefits
The biomimetic adhesive materials developed by NUK have the following benefits and features:
- Residue-free adhesion
- High strength adhesion and control of adhesive strength
- Re-usable adhesive surfaces
- Suitable for use at high temperatures
Project Status
This is project is at TRL 5 and the technology has produced prototype adhesives that are undergoing industrial trials. Patents covering the technology are in force.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
James Hudson, PhD
E: james.hudson@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7971 515869
Novel enzyme with high specificity for the high-yield production of lactobionic acid from lactose.
Available to license
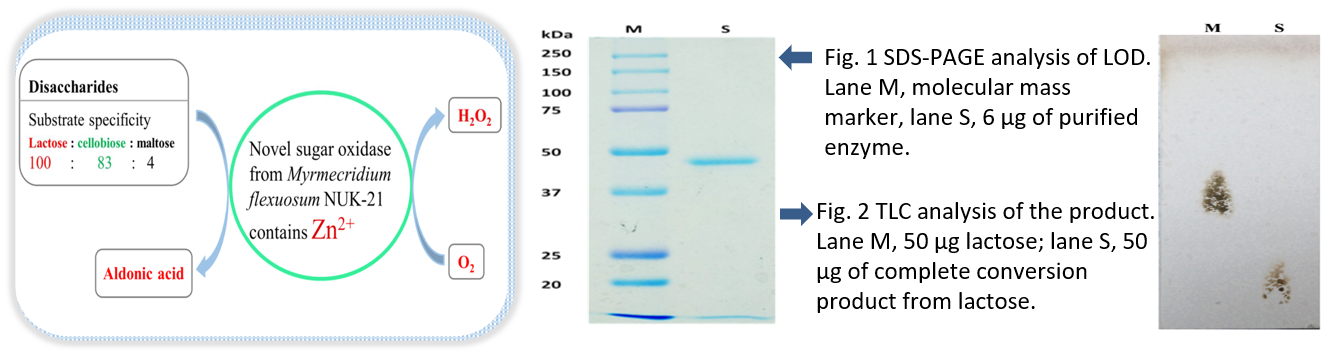
Introduction
Lactobionic acid has been deployed in a wide range of applications in the pharmaceutical, food, nano-technology and chemical industries. Its production may be achieved by the enzymatic conversion of lactose in a bioreactor. A research team at the National University of Kaohsiung (NUK) in Taiwan has isolated a novel oxidase enzyme from the fungus Myrmecridium flexuosum that produces higher yields of lactobionic acid from lactose when compared to existing enzymes.
The NUK Team is now looking to commercialise this enzyme via its inclusion in industrial processes.
Our Technology
Research at NUK has identified and extracted a novel zinc-based enzyme from that is able to catalyse the production of lactobionic acid from lactose.
This newly discovered lactose oxidase from Myrmecridium flexuosum differs from previously reported ones in several regards: it has a lower molecular weight, a higher substrate specificity in respect of other sugars, and has a metal prosthetic group. It is considered to be of great industrial relevance due to its low Km and high Kcat values and may therefore also be used for lactose and cellobiose quantification.
The research group is now studying the optimal submerged conditions of the MF for enzyme production, optimal conditions for the optimal immobilisation of lactose oxidase and catalase onto chitosan beads, and optimal bioreactor systems for production of lactobionic acid with industrial use in mind.
Features and Benefits
The novel lactose oxidising enzyme has the following features and benefits:
- Simplified extraction compared with microbial fermentation
- The enzyme produces lactobionic acid at higher yields than competing enzymes
- High reactivity and high specificity
- Activity is highest at near neutral pH levels
- Resistance to inhibition by chelating metals and hydrogen peroxide
Project Status
This is project is at TRL 4. The technology has been validated at laboratory scale. Patents covering the novel enzyme have been filed in the USA and Taiwan.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
James Hudson, PhD
E: james.hudson@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7971 515869
Low-cost, real-time imaging of live cells for a wide range of applications including circulating cancer cell detection and drug efficacy studies
Available to license
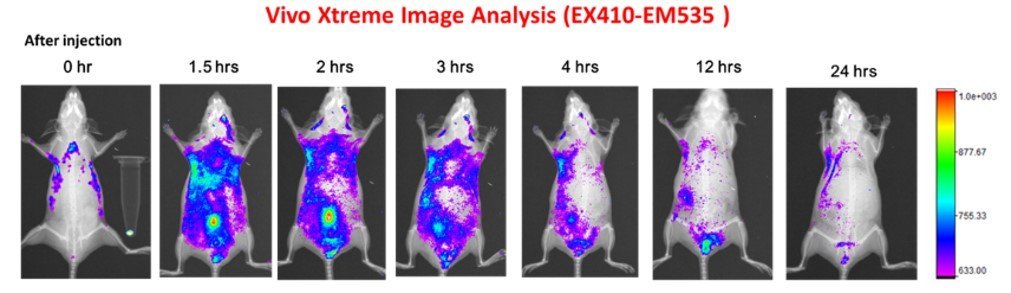
Introduction
A new saccharide-based fluorescent probe (SFP) is synthesised for detecting cancer cells and many other applications. Within two hours, several types of circulating tumour cells can be identified and/or information relating to changes in viability of living cells will be obtained.
Applications of this technology include: cancer diagnosis, fluorescent guide tumour margining, micro-organisms detection, drug screening, toxicity assay for new drug development.
Our Innovation
Non-invasive, biomedical imaging techniques are widely used to detect cells or molecules for cancer detection, microorganism detection, and drug development.
This new technology uses fluorescent saccharide-based derivatives obtained from amino sugar compounds to track and monitor cells in real time. Cancerous, damaged and healthy cells absorb the saccharide-based fluorescent probe to varying extends due to intrinsic differences between the cell types.
Existing detection technologies are limited by constrains on the volume of samples that can be processed in a single batch. Some existing detection technologies require cells to be killed, which limits potential applications. Others require expensive equipment such as Positron emission tomography(PET) which is not real time and also cause cell damage.
Features and Benefits
The fluorescent saccharide-based derivatives detection system has the following advantages:
- Fast: results available in two hours;
- Low-cost and easy to operate: compound synthesis and imaging use standard, low-cost techniques;
- Biocompatible: not toxic to cells.
- Versatile: cells kept alive during imaging allowing for applications in drug screening and precision medicine.
Project Status
This project is at TRL 4/5-a small scale GLP production of SFP powder has been developed. Patents covering the novel composition and detection have been filed and granted in the USA and Taiwan.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Ms Ya-hsin Shen, Senior Consultant
E: ya-hsin@oxentia.com
T: +852 63054387
An improved inner ear vestibular examination system
Available to license
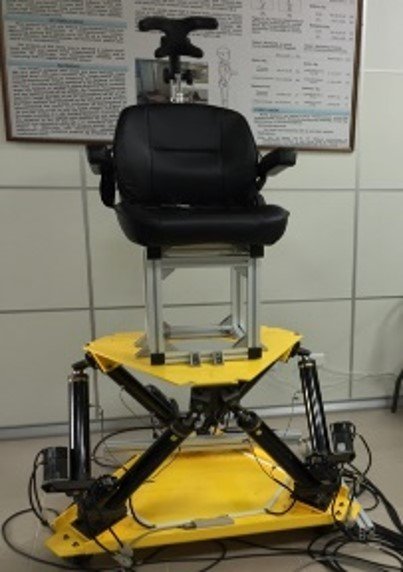

Introduction
In the US, there are approximately 69 million Americans (35% of adults aged 40 years or older) have experienced some form of vestibular dysfunction. Researchers have invented a system to improve existing methods of measuring inner ear function with better results, which are collected automatic and interpreted objectively.
Applications of this device include: vestibular examination, measurement of dizziness and balance disorders, and facilitating rehabilitation of vestibular function.
Our Technology
The vestibular disorder is the major cause of dizziness in older people. Dizziness may lead to falls which are a leading cause of death, injury and hospital admissions: one out of every four Americans aged 65 and older fall every year. Vestibular disorders not only affect the elderly and adults but also children and these incidents affect daily routines, work and social life of people with the condition.
Researchers at KMU have developed a vestibular examination system, including a seat movably with six degrees of freedom and detectors for patients’ eye movement. It provides a quantitative impulse motion to replace head impulse test (HIT), which is currently performed manually by clinicians for vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The electrooculography data collected is then used to identify if a patient has any vestibular dysfunction and nystagmus.
The device can also be used to provide rehabilitation programmes with potential markets in both clinical and consumer wellness.
Features and Benefits
This new vestibular examination system has the following advantages:
- Improved test efficacy: existing devices are able to assess movements in only one dimension
- Improved automation: non-automated HIT practice is very delicate and requires greatly experienced clinicians
- Objective test results: results from current HIT tests are often incomparable
- Dual functions for both examination and rehabilitation
Current Status
This project is at TRL 7. A prototype of the system is available and has been verified. Patents have been filed in Taiwan and the USA.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Ms Ya-hsin Shen, Senior Consultant
E: ya-hsin@oxentia.com
T: +852 63054387
Optimising virus titer for quicker and cheaper vaccine development
Available to license, collaborate and invest
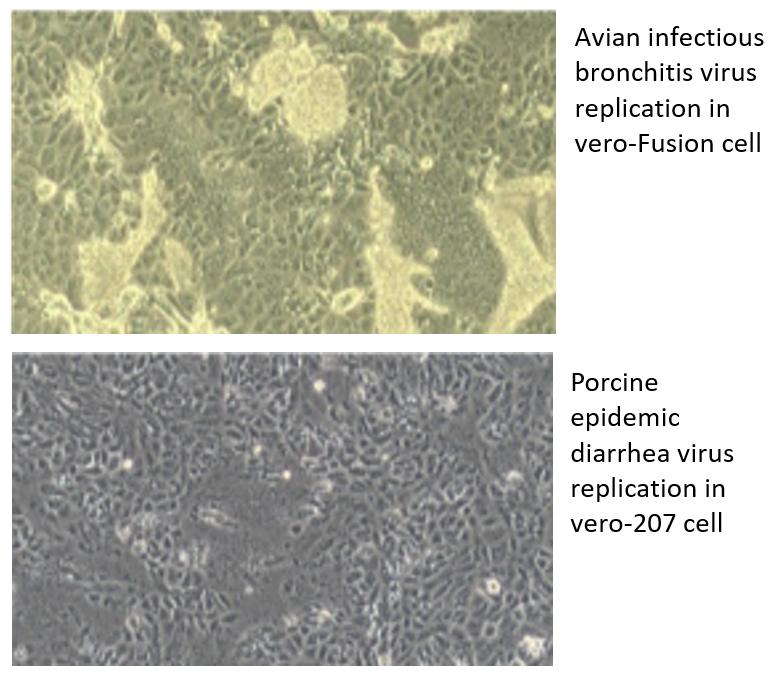
Introduction
Immunisation is one of the most successful and cost-effective public health interventions: over two billion doses of vaccines were given worldwide in 2017. A platform to grow viruses in suitable cells for various vaccines has been developed and verified; it allows vaccine development to be undertaken at larger scales and at lower costs in a tractable environment which does not use animals.
Potential applications of the technology include both human and animal vaccines.
Our Innovation
Cell culture is an important gold-standard technique for modern vaccine manufacturing at industrial scales. To allow vaccines to be made at lower costs and greater potential availability for people in need, viral yield is paramount.
For viruses to replicate in cells, the cell culture process has to match the properties of the virus-host cell system (including elements such as cell line, culture medium, and bioreactor). Over the last ten years, the team at NPUST has focused on selecting cell and virus clones for maximum levels of viral replication. Natural variants in cell and virus clones are used and the ideal combinations of virus and host cells are screened to optimise virus titer.
Viral replication in cell culture is a complicated biological system. This technology allows vaccine researchers, developers, and manufacturers to evaluate a wide range of cell lines for the development of new vaccines as well as the improvement of existing ones. This is done to higher quality standards at lower costs.
Features and Benefits
The virus and cell culture platform has the following key advantages:
- Simple: standard cell culture equipment, no need for additional cell treatments or growth factors.
- Proven technology: has been used in virus attenuation and adaptation for important viruses, including influenza, Newcastle disease, PRRS, Avian reovirus, Infectious bursal disease, and PED.
- Cheaper and quicker vaccine production.
Current Status
This project is at TRL 7 – around 30 cell lines and 50 viruses have been developed via this platform, including several which are currently undergoing commercial validation.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcome contact from parties interested in commercialising this technology. The team is exploring several options including grant of licence and new venture creation. A product catalogue is planned. Contact us with any queries or if you would like more information.
Ms Ya-hsin Shen, Senior Consultant
E: ya-hsin@oxentia.com
T: +852 63054387
Graphene oxide solutions at exceptionally high concentrations from agricultural waste
Available to license

Introduction
Graphene-based materials have a wide range of applications in thermo-/electro- conducting, energy storage, biomedical, environmental, and semiconductor applications. Researchers have developed a new method to produce a 30% by weight solution of graphene oxide from biomass, for example agricultural wastes. The process is able to generate high-purity graphene sheets at low production costs.
Our Technology
Graphene is a novel but highly prized nanomaterial because of its unique and desirable properties suited to many industrial interesting. However, there is no method of synthesis currently available for continuous mass production. Graphene oxide (GO) solution is one popular alternative to produce reduced GO (rGO) powder which has similar structure and properties as graphene but is easier and cheaper to make in large quantities. Or directly use GO solution as processing raw material for industrials.
GO solution is commonly manufactured by Hummer’s method using either natural or synthetic graphite. Synthetic graphite usually costs several times more than natural graphite.
Researchers at NPUST have developed a method to extract micro-graphite content from biomass after a properly conversion into biochar, in an environmental friendly manner. The method offers a solution to discard lignocellulose solid waste with no air pollution or intense labour and, at the same time, it provides source materials in producing high-quality rGO.
Features and Benefits
This new method for producing GO solution has the following advantages:
- High concentration GO solution of 30wt% provides superior value and reduces transportation costs
- Graphene sheets with fewer inorganic impurities compared with other natural graphite sources
- Avoids highly polluting processes currently used in treating natural graphite
- Low production cost as a result of low level of secondary pollutants
- Reduces agricultural wastes which otherwise leads to air pollution and increased disposal costs
Current Status
This project is at TRL 5. The operational parameters for producing both biochar (30 kg/week) and GO solution (10L/week) have been developed in laboratory environments. GO solution needs to double for industrial applications.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Ms Ya-hsin Shen, Senior Consultant
E: ya-hsin@oxentia.com
T: +852 63054387
An improved outer casing to prevent heat flux: simple and easily manufactured
Available to license

Introduction
Rockets and satellites are used for multiple military and civilian applications. Researchers have improved the commonly used yo-yo despin mechanism with a simple and easy-to-manufacture outer casing to prevent heat flux as a result of high speed. The new design has been tested on a sounding rocket and is ready to be implemented in other rockets and spacecraft.
Our Technology
Space is a huge industry. Indeed, weather applications alone amount to a multibillion market. Space satellites are the primary tools for a range of purposes such as observation, communication, navigation, and scientific missions. Recently, Very Low Earth Orbits (VLEO) have further augmented this already large market with new applications and increasing numbers of cheaper launches.
Satellites and other spacecraft are transported by rocket-powered launch vehicles into orbits or other space destinations. Launch costs constitute a major proportion of the total costs.
Researchers at NPUST have developed a new yo-yo despin device with an outer casing that improves launch performance. Traditional yo-yo despin devices has been used by the industry since the 1960s but the new design can reduce the heat flux of a launch vehicle between take-off and the jettisoning of the satellite or spacecraft.
Features and Benefits
The new yo-yo despin device has the following advantages:
- Simple and cost effective: compared with other methods to reduce heat flux, the new design is based on existing yo-yo despin devices but adds a simple outer casing.
- Improved launch performance: the new design prevents potential damage to rocket circuits and sensors.
Current Status
This project is at TRL 9. The new design has been implemented and tested on a real-world sounding rocket, SR-10, in Taiwan in 2014. Patents have been filed and granted in Taiwan and the USA.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Ms Ya-hsin Shen, Senior Consultant
E: ya-hsin@oxentia.com
T: +852 63054387
Direct-drive generator turbine design for improved capture of wind energy
Available to license or co-develop
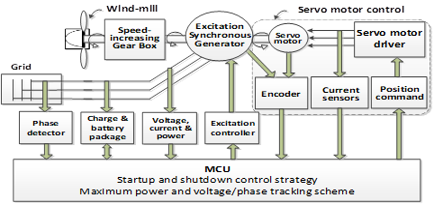
Introduction
Wind power has seen rapid uptake over the past two decades due to its ability to provide sustainable energy in place of fossil fuels. Limitations with conventional wind generators are the energy losses that occur during DC to AC conversion and power generation often ceases entirely when wind speeds are above or below a defined range. A research team at the National Sun Yat-sen University (NSYSU) in Taiwan have developed a direct drive synchronous power generator that can be connected directly to the electricity transmission network. This generator design provides a disruptive solution to the issues currently leading to energy losses in wind-powered generation.
The NSYSU research team are now seeking to commercialise this disruptive technology.
Our Technology
Research at NSYSU has generated solutions to overcome energy loss issues in wind generation using conventional generator configurations.
This research has culminated in a radical rethink of generator design which has led to a direct drive synchronous strategy and control system. Using a phase tracking control strategy, the proposed system achieves smaller voltage phase deviations and the maximum output power tracking scheme governs the input and output powers to achieve high performance. With this design, constant rotation speed of the turbine is provided via a servo motor enabling power conversion of up to 97%.
The research group is now increasing the accessibility of this technology by exploring a scaled-up prototype and is searching for industrial partners.
Features and Benefits
The direct drive, synchronous wind generator control mechanism provides the following features and potential benefits:
- Increased conversion of wind energy by broadening operational wind speed range
- Reduced energy losses in transmission
- Low maintenance requirements
- Cost-effective design
Project Status
This is project is at TRL 3-4. A lab-scale demonstrator exists and this has been used to validate the principal. Patents covering the technology are in force including in the USA.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Ms Ya-hsin Shen, Senior Consultant
E: ya-hsin@oxentia.com
T: +852 63054387
Customisable porous, ceramic sintered structures with beneficial mechanical properties for biomedical applications
Available to license
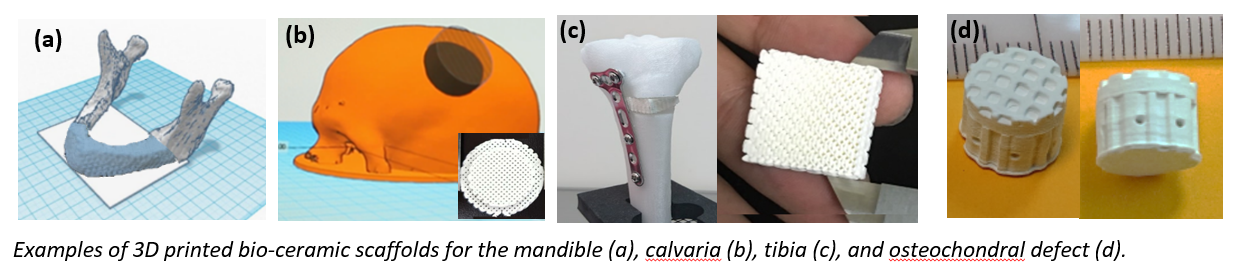
Introduction
3D printed bio-ceramic scaffolds are commonly used in biomedical engineering research as a base to repair bone tissues due to their porosity, pore connectivity, and orientation. However, current bio-ceramic of calcium phosphates have poor biomechanical properties. Although they are printed in a similar shape with pore connectivity to fit the bone defect geometry, they are often unable to replicate the appropriate biomechanical properties such as the critical factor of strength. Attempted improvements in strength often reduce biocompatibility or biodegradability and therefore cannot be used. Research from Kaohsiung Medical University addresses these issues through a unique manufacturing method which has uses in various biomedical bone scaffold applications.
Our Technology
The novel methods employed in this technology can enhance the mechanical properties of bio-ceramic scaffolds. These enhancements are derived from the mixture of a combustible reverse negative thermo-responsive hydrogel that burns away during sintering in the creation of the bio-ceramic scaffold. The sintering encourages densification of the bio-ceramic which improves the mechanical properties.
This technology uniquely provides the exact pore size required for cell conductivity. This allows incorporation with a calcium phosphate bio-ceramic system which represents a promising approach for anatomic bone engineering. Additionally, future zirconia and alumina ceramic devices could be created using this novel 3D printing of ceramic technology. These bio-ceramic devices may offer additional benefits for bone or prosthodontics. This technology seeks to facilitate the fabrication of more precise and complex shapes using 3D printing of ceramic technology.
Features and Benefits
The 3D printed bio-ceramic scaffolds has the following advantages:
- Customisable
- Faster processing time
- Superior mechanical properties compared with other 3D printed bio-ceramic
Project Status
This project is at TRL 4-5. A bone defect model was 3D printed using the patented technology and tested in an animal model. More work and funding are required to make the technology and resulting product market ready. Patents covering the novel technique have been granted in Taiwan and the US, published in Japan, and are under examination in China and Europe.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Janice Ng, PhD
E: Janice.ng@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7387 261606
A new, environmentally friendly PEM fuel cell with excellent durability and efficiency
Available to license

Figure 1. Application of hydrogen fuel cell in car and bus
Introduction
Hydrogen fuel cells are one of the promising technologies for reducing carbon emissions from vehicles. Proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells are the most common and the 2019 market size for PEM fuel cells is USD2.75 billion. They are used in cars, buses, and consumer electronic devices (Figure 1). Researchers have developed a new PEM fuel cell using a novel polymer electrolyte which can be easily applied to catalyst layers using cheap and simple manufacturing processes.
Our Technology
Fuel cells generate electricity from hydrogen using a clean, emission-free chemical process and are 2-3 times more efficient than internal combustion engines. Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) fuel cells use PEM as an electrolyte to improve the electrochemical conversion efficiency and they are the most common fuel cells on the market.
However, most of the existing PEM cells contain substances harmful to the environment.
Based on over 20 years of experience, researchers at NSYSU have invented a new PEM fuel cell using sulfonated aromatic hydrocarbon polymer. The team has also developed a manufacturing process of the fuel cell catalyst layer based on these sulfonated poly(arylene ether)s. The manufacturing method uses spray or spin coating which simplifies the manufacturing process and reduces costs.
PEM fuel cells are expected to achieve significant market uptake in cars and buses within the next five years. Other deployment is anticipated within sensitive electronic appliances such as cell phones, laptop computers, and digital cameras.
Features and Benefits
The new PEM fuel cells have the following advantages:
- Environmentally benign
- Good product durability: sulfonated poly(arylene ether)s have good thermal stability, mechanical properties, and chemical resistance
- Excellent cell efficiency: sulfonated poly(arylene ether)s can effectively facilitate proton transmission
- Low-cost production
Project Status
This is project is at TRL 5 – the technology has been demonstrated on single cell and the current creation capacity in the lab is 10kg. Patents are granted in Taiwan and the US.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Janice Ng, PhD
E: Janice.ng@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0) 7387 261606
For improving insulin resistance and glucose metabolism or as an anti-diabetes and anti-obesity supplement
Available to license and seeking commercial partner

Figure 1: Bacillus amyloquefaciens (left; the bacterial
powders) and its exopolysaccharides (EPS) (right;
dried powders) can be produced by fermentation.
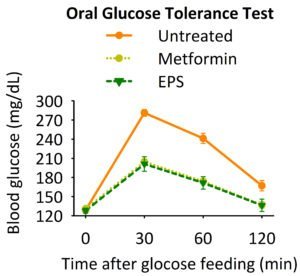
Figure 2: Mice were fed with water (untreated), metformin
(an anti-diabetes medicine), or EPS, followed by feeding
of glucose. Blood glucose was measured at 0, 30, 60,
and 120 min post glucose feeding.
Introduction
Diabetes is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in all around the world; The World Health Organisation projects that it will be the 7th leading cause of death in 2030. Researchers have identified a biomacromolecule with the potential as an anti-diabetes treatment; experimental data to date show promising results in its ability to lower blood glucose (Figures 1 and 2) .
Our Technology
Diabetes results in raised blood sugar if left untreated, this hyperglycaemia can cause serious damage to multiple body systems including in particular the nerves and blood vessels. The cause of diabetes is multi-factorial and most medications available at the moment only address individual pathologies. The disease can also evolve in many different ways making treatment plans a difficult especially given that the limited number of medications become ineffective in some cases.
Researchers at NPUST have discovered that exopolysaccharides (EPS) of Bacillus amyloquefaciens can lower blood glucose in animal experiments. EPS was found to promote glucose uptake and at the same time promote insulin secretion. This makes it an ideal anti-diabetes drug candidate.
The effects of these polysaccharides can potentially benefit both insulin-independent type 2 diabetes patients (95% of cases), and insulin dependent type 1 patients by replacing insulin injections.
Features and Benefits
The proprietary polysaccharides have the following advantages:
- Ability to lower blood glucose: with potentially superior results due to its two-fold mode of action
- Cheap and easy to manufacture: B. amyloquefaciens is easy to culture by fermentation and grows fast
- Potential as an anti-diabetes treatment as well as an anti-obesity treatment
- B. amyloquefaciens is an approved probiotic for animals in the EU and confirmed to be non-harmful to humans in the USA.
Current Status
This project is at TRL 2. The benefit of EPS in modulating blood glucose in humans has not yet been proven. Large-scale production is yet to be implemented.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Janice Ng, PhD
E: Janice.ng@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7387 261606
Flexible roll forming machine for creating intricate cross-sectional profiles
Available to license

Figure 1. A prototype of flexible roll forming machine
controlled by a proprietary ethernet control system for
manufacturing high tensile steel products. The modular
machine has three forming stands and three feeding guides.
Introduction
Roll forming is widely used by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to manufacture constant profile parts with long lengths and in large quantities. However, current designs of roll forming machines have limitations in their flexibility to create more intricate profiles.
A research team at National Kaohsiung University of Science and Technology (NKUST) in Taiwan has developed a 3D flexible roll forming machine with a proprietary ethernet control system. This machine allows rapid manufacturing of high tensile steel products with a large diversity of different profiles (Fig. 1).
Our Technology
Researchers at NKUST have sought to improve roll forming machines for the manufacturing of intricate cross-section profiles. The developed roll forming machine are well place to be deployed in many manufacturing industries and it can be connected with computer numerical control (CNC) systems.
To form intricate cross-sectional profiles, the research team has designed a three-dimensional flexible roll forming process with precision control compensation that is managed by proprietary control software. The rolling process is driven by multiple linear and horizontal rotating units and roll sets which are sequentially stacked at optimal angles to ensure smooth rotation for flexible rolling.
Project Status
This project is at TRL 7. A prototype roll-forming machine has been used to manufacture high tensile steel products (Fig. 1). Interested parties can license the patented technology to incorporate into their own precision manufacturing flows. The technology has a patent in Taiwan. The publication number and date of the patent is TWI632960B (21 Aug 2018).
Features and Benefits
The flexible roll forming technology provides the following features and potential benefits:
- Speed and flexibility: Creation of intricate cross-sectional profiles. Details of profiles can be uploaded to the machine through proprietary software.
- Convenience: Sets of rollers to create a variety of cross-section profiles. No change of rollers is required.
- Scalable: Each forming station has an independent control system and these can be connected to build a network of forming machines.
- Backlash reduction: System design that reduces accumulated errors during forming processes.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Janice Ng, PhD
E: janice.ng@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7387 261606
Superior accuracy and efficiency in detecting anomalies through advance image recognition and lighting compensation
Available to license

Introduction
The overall Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) System market is expected to reach USD 1.6 billion by 2024, up from USD 0.4 billion in 2018. The increasing need for high-quality products; faster and real-time vision-based inspection during production has created a huge demand and drive for the implementation of AOI systems. However, current AOI systems have limitation in low light detection and high rate of false alarms in anomaly detection.
A research team at National Kaohsiung University of Science and Technology (NKUST) in Taiwan has developed an AOI system that provides superior accuracy and efficiency in detecting anomalies. The NKUST research team is now planning to licence this AOI-Smart technology.
Our Technology
Researchers at NKUST have created an improved AOI system for detecting anomalies more accurately and efficiently. In addition to being of special relevance to the quality control of plastic, glass and metal surfaces (Figure 1) the technology is applicable to the following industries:
- Special parts manufacturing
- Consumer and industrial products
The AOI-Smart System is also applicable to image and face-recognition technologies (Figure 2).
The AOI-Smart system is composed of the following 5 technological components including a proprietary mathematical algorithm.
- Light field design
- Image capture
- Lighting compensation
- Defect detection
- Defect classification
This system can be customised and complemented to achieve compatibility with existing manned and unmanned systems.
The research team has recently received further funding for ongoing product research and development to improve the features of system.
Features and Benefits
The AOI-Smart system provides the following features and potential benefits:
- Unmanned
- Low rates of false alarm
- Sensitive in detecting dissimilarities
- Efficient in detecting invisible defects
- Extremely customisable
Project Status
This project is at TRL 7. The technology has been demonstrated to detect anomalies in ophthalmic glass, mobile phone panels, and roll-to-roll steel surfaces. It has also been tested for use in deformation measurement for convex car mirrors and in systems for marking exam papers.
Interested parties can license the proprietary mathematical algorithm for incorporation into their inspection systems.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Janice Ng, PhD
E: janice.ng@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7387 261606
A novel formulation for promotion of hair growth
Available to license
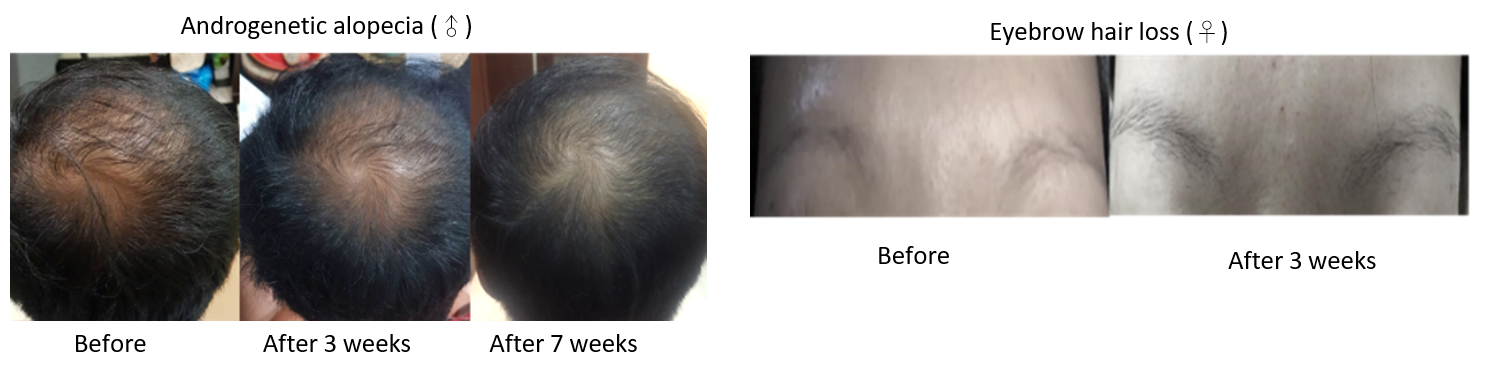
Figure 1: Proprietary Derinat formulation from Kaohsiung Medical University (KMU) promotes and maintains hair growth
Introduction
Worldwide, over 800,000 patients seek some kind of hair loss treatment every year, with a projected market size of USD900 million by 2023. Researchers have found a new use of an existing clinical drug with excellent results for hair growth treatment in animal models. The agent can promote hair growth and protects hair and skin from oxidative stress in the ageing process.
Our Technology
In the US, about 85% of men and 40% of women by the age of 50 experience thinning hair. Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, is a medical condition that refers to loss of hair from head or any part of the body. Hair loss has high prevalence in working age population and is often caused by hormonal changes and ageing. Currently, there are very few approved drugs for the effective treatment of hair loss.
Researchers at Kaohsiung Medical University (KMU) have discovered that a formulation containing the chemical known as Derinat, when combined with an appropriate application regime, can promote hair growth by activating hair follicle stem cells. The treatment also protects hair follicles and skin tissue from endogenous oxidative stress by blocking intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Derinat is commonly used as immunomodulator, and is a popular drug in Russia. However, Derinat is not currently used in hair loss treatments.
Features and Benefits
The Derinat formulation and application regime for hair loss treatment has the following advantages:
- Promotion of hair growth by activating hair stem cells;
- Passively prevention of hair follicles death due to aging;
- No toxicity;
- Water solubility for flexible formulation
Current Status
This project is at TRL 5-6: Animal trials have been completed. A small human trial is currently ongoing. Patents have been filed in Taiwan and the USA.
Next Steps
Oxentia welcomes contact from parties interested in receiving further information:
Janice Ng, PhD
E: Janice.ng@oxentia.com
T: +44 (0)7387 261606